



Sound changes frequency with source or observer movement {Doppler effect}|.
stationary case
When stationary sources emit sounds or light waves with one wavelength and frequency, stationary observers hear one pitch or see one color. See Figure 1. Only wave moves, at constant velocity, because medium does not change.
Source x emits maximum positive amplitude, a line in the diagram, once each cycle. In the diagram, wave travels left two spaces for each cycle line. From one cycle line to the next, observer encounters one peak. There is no Doppler effect.
moving-toward case
When sound-wave or light-wave source moves toward stationary observer, or observer moves toward stationary wave source, observer hears pitch increase or sees shift toward blue color. This is Doppler effect. When frequency increases, wavelength decreases, because only sound medium or electromagnetic-induction speed determines constant wave velocity. See Figure 2.
In the diagram, observer travels right one space for each line, at half wave speed. Observer movement brings it closer to next wave peak. From one line to the next, observer encounters one and one-half wave peaks. Frequency has increased.
See Figure 3. In the diagram, source travels left one space for each line, at half wave speed. Source movement brings it closer to previous wave peak. From one line to the next, observer encounters two wave peaks. Frequency has increased.
moving-away case
When sound-wave or light-wave source moves away from stationary observer, or observer moves away from stationary wave source, observer hears pitch decrease or sees shift toward red color. When frequency decreases, wavelength increases, because wave speed is constant. See Figure 4.
In the diagram, observer travels left one space for each line, at half wave speed. Observer movement brings it farther from next wave peak. From one line to the next, observer encounters one-half wave peaks. Frequency has decreased.
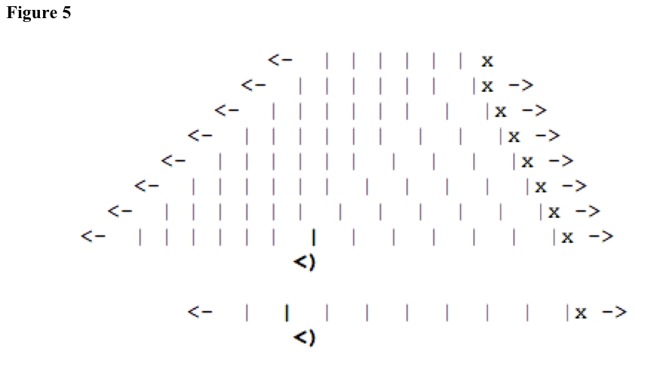
See Figure 5. In the diagram, source travels right one space for each line, at half wave speed. Source movement brings it farther from previous wave peak. From one line to the next, observer encounters two-thirds wave peaks. Frequency has decreased.
examples
As sound-emitting vehicles move closer, sound has higher pitch. As they move away, sound has lower pitch.
As light-emitting stars and galaxies move away from Earth as universe expands, Doppler effect makes emitted light have decreased frequencies, so light becomes redder {red-shift}.





Physical Sciences>Physics>Wave
Outline of Knowledge Database Home Page
Description of Outline of Knowledge Database
Date Modified: 2022.0224